April 21, 2021 | Advanced Manufacturing, Additive Manufacturing, Future of Manufacturing
Top 8 Industries Benefiting from Additive Manufacturing

Additive manufacturing (AM), or 3D printing, has evolved rapidly in recent years. As new industries have begun to embrace the technology, they are discovering the many ways in which their business is being impacted by it. Additive manufacturing technologies are continuing to evolve at a fast pace, leading to new additive applications being developed. These new processes, along with a growing range of production-grade materials, such as titanium, steel, and a range of plastics, enable a wide range of capabilities.
With all these applications of additive manufacturing, numerous industries are capable of reducing development and manufacturing costs while increasing production, speed, innovation, and time-to-market. It’s also possible to produce new structures and shapes—all the while decreasing waste. Read on to learn more about these eight industries reaping the benefits of additive manufacturing and the future of this technology.
Quick Links:
- What is Additive Manufacturing?
- What is the Additive Manufacturing Market Size in 2021?
- Top Industries Benefiting from Additive Manufacturing
- Interested to Learn More About the Benefits of Additive Manufacturing?
What is Additive Manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is the process of creating a three-dimensional object from a digital 3D or CAD model. As is implied by the name, additive manufacturing works by adding materials to create an object by building it layer by layer. These materials can include metal powders, plastic, or ceramics. Additive manufacturing can augment, and in some cases, totally replace traditional methods of creating objects by machining, cutting, turning, shaping, milling, and other “subtractive” manufacturing processes.
During the additive manufacturing process, the object is designed using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software or by taking a scan of the object that will be printed. The software can translate the scan into a precise framework for the 3D printing machine to follow layer by layer.
What is the Additive Manufacturing Market Size in 2021?
As advancements in additive manufacturing continue to make this process more accessible than ever, an increasing number of industries are implementing 3D printing in their operations. As it stands, additive manufacturing technologies are looking to be a highly disruptive force throughout the entire global manufacturing industry. The global additive manufacturing market size is projected to be sized at $30.6 billion in 2028. Other reports estimate the market to grow by a high rate of 14.4% a year. It’s expected that manufacturing will garner nearly 33% of the total market share by 2027.
The driving force behind this rapid growth is the ability of additive manufacturing technologies for companies to shift from prototyping applications to efficient mass production of parts, components, and accessories. With advancements in AM technologies coupled with the growing adoption of additive across various industries, it’s likely that the market will continually expand.

Top Industries Benefiting from Additive Manufacturing
As new applications of additive manufacturing continue to be made available, more industries have embraced AM technologies. Here are some of the top industries currently developing and producing additive manufacturing applications that were previously unattainable just a few years ago.
Aerospace
Always on the cutting edge, the aerospace industry was an early adopter of additive manufacturing. Aerospace companies must meet some of the manufacturing industry’s most stringent standards, and parts and components need to be made of the highest-performance materials. Using AM, engineers can design complex, high-strength parts while also reducing the weight of aerospace components by printing more efficient geometries and eliminating significant amounts of unnecessary material. This allows for lower fuel consumption, reduced CO2 emissions, and reduced costs (plus, better airfares).
Automotive
Much like aerospace, the automotive industry is always looking to innovate with newer designs; their products are also subjected to high speeds and harsh conditions. AM allows them to develop complex, high-quality parts that can withstand these conditions, offering improved safety. Rapid prototyping also improves vehicle quality, enabling automobile manufacturers to test things like water resistance and high temperatures. In addition, 3D printing allows for parts consolidation, reducing inventory, and enabling repair or maintenance to be done with a single part. And, like in aerospace, AM technologies allow for lattice structures to be printed so car parts can be as lightweight and aerodynamic as possible.
A real-life example of 3D printing in the automotive industry is how Porsche now supplies parts of rare classic cars through a 3D printer. Where collectors would have a difficult time finding outdated parts for their cars, 3D printing allows spare parts to be printed for rare vehicles.
Consumer Products
For marketing teams taking a product from concept to completion, often the biggest amount of time is spent on design. To be sure the product is just right, a great deal of time is spent on creating prototypes to prove concepts to stakeholders and ultimately deliver a consumer-pleasing product.
By embracing AM, marketing teams can develop iterations of their product much quicker, and then rapidly pivot to adjust the design as needed. As additive manufacturing continues to advance with build volume and speed, more consumer products may be produced through AM technologies for quick and efficient mass production demands.
Energy
Electrical power outages, surges, and spikes are estimated to cost more than $150 billion in annual damages to the United States economy due to labor downtime and loss of productivity and data. Using additive manufacturing, the energy sector can create lightweight, efficient, and environmentally-friendly components that can also withstand extreme conditions. Plus, AM technology can allow for the development of corrosion-resistant metal materials for customized parts that may need to experience underwater or other harsh environments.
Besides the possibility of developing superior products, additive manufacturing adoption for the energy industry entails the use of newer and lighter materials. And, with AM technologies reducing production costs by 40% and the time to market by one-third, the energy industry is expected to invest significantly towards additive manufacturing in the future.
Infrastructure
Imagine walking over a bridge made entirely from 3D printing. Soon, this may become reality. In fact, it already is in the Netherlands where the world’s first 3D-printed pedestrian bridge was unveiled in 2018. The structure was created by additive robotics layering molten steel and measures nearly 40 feet across.
Additive manufacturing in the construction market is expanding, ushering in a new era for the industry. According to a study by Transparency Market Research, 3D printing in the infrastructure secretary is predicted to expand at a CAGR of 33 percent by 2027. Since printed materials can be precisely applied layer by layer when building infrastructure or constructing buildings, AM reduces material waste and allows construction to be as cost-efficient as possible.
Additionally, 3D printing technology allows for complex design structures since the materials are printed precisely - reducing the likelihood of infrastructure accidents from construction mistakes and poor design. While 3D printing is not being employed in everyday bridge building, there is plenty of future potential as the industry expands. And, with a recent report finding that over a third of all U.S. bridges need major repair work or should be replaced, there may be a rapid expansion of the industry in the near future.
Medical & Pharmaceutical
Additive manufacturing has revolutionized the medical industry, turning what was once science fiction into a new reality. The technology is delivering breakthroughs to doctors, patients, and research institutions. From durable prosthetics and true-to-life anatomical models to surgical grade components, the incredible plethora of objects that have already been successfully printed in the medical field gives a glimpse into the potential that this technology holds for healthcare in the near future.
For example, additive manufacturing allows for 3D printed dental appliances and custom-made devices, such as dentures, crowns, and even Invisalign™, to be constructed from a variety of substrates and prints customized to each individual. Currently, the 3D printing market for digital dentistry is valued at $2.5 billion — and is expected to only keep growing. Additionally, additive manufacturing allows for devices such as hearing aids that can be mass-produced made for a better fit to ensure the highest level of comfort for the user.
One of the latest ongoing projects is the use of additive technology by researchers to print human embryonic stem cells. By doing so, these stem cells can then be used to create tissue for testing drugs or growing replacement organs, to print skin that could replace skin that’s been burned or damaged, and to print cancer cells to study and test out new drugs on them. Surgeon Anthony Atala, Director of the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, has even been working on printing organs, believing that printing an organ may soon replace transplanting an organ.
Edible Goods
Additive manufacturing holds the potential to shake up the food industry. While additive manufacturing is less an industry game-changer currently in the food industry, edible AM printing holds a wealth of opportunity. As of now, chocolates and even pizza are capable of being 3D printed.
Binder-jetting is one of the more common methods of 3D printed food production. By replacing the metal powders and polymers with crystal sugars to design and create complicated, precise sugar sculptures, especially for restaurants, bakeries, and hotels. Edible additive printing presents branding opportunities for producers of candy and sweets since 3D printing allows for precisely drawn logos and photos.
There are also the possibilities that additive manufacturing in edible foods may be able to lead to the creation of unique food formulations for dietary needs, simplified distribution into hard-to-reach locations, and customized medical/nutritional supplements.
Sports
The sports and games manufacturing world is being impacted by 3D printing in the creation of fashion, gear, and accessories. The sports goods industry makes about $45 billion dollars annually in the United States alone, and additive manufacturing offers numerous advantages. Since 3D printing enables customization and personalization, sporting goods manufacturers are now developing personalized equipment for athletes that are custom-tailored to their exact measurements. Sports equipment can also now be manufactured to be lighter but just as strong, if not more so.
Additive manufacturing also provides opportunities for better safety gear due to stronger materials and intricate geometric designs. Football helmet manufacturers are always looking for ways to improve helmet designs to prevent head trauma. With 3D printing’s ability to create lattice structures, the final product is not only light, but enables safer pressure distribution for physical helmets. Along with the ability to customize each helmet for the athlete’s exact head shape, 3D printing can produce a superior helmet.
Foodware companies, from Adidas to Nike, are utilizing additive manufacturing to create custom-fitting shows that enable a better grip and fit and both better insoles and exteriors. While a completely 3D printed shoe is not currently on the market, 3D printing is involved in the making of many athletic shoes today and will likely continue to grow in this industry.
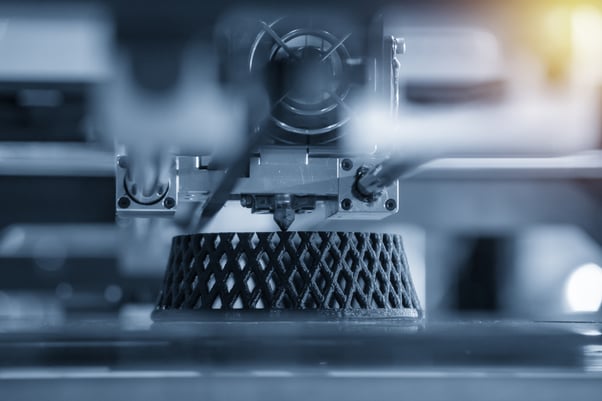
Interested to Learn More About the Benefits of Additive Manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing is a game-changer for manufacturers of all sizes. It can enable them to create products faster and cheaper—but with less production waste and better precision. When you look at the bigger picture, AM is also changing the lives of everyday Americans, from medical breakthroughs to safer transportation and roadways.
You can start growing your business today with additive manufacturing! If you don’t know where to start, reach out to our experts today! CMTC is here to help guide small to medium-sized manufacturers towards solutions that can impact their business for sustainable and impactful growth.
About the Author
Gregg Profozich
Gregg Profozich is a manufacturing, operations and technology executive who believes that manufacturing is the key creator of wealth in the economy and that a strong manufacturing sector is critical to our nation’s prosperity and security now, and for future generations. Across his 20-year plus career in manufacturing, operations and technology consulting, Mr. Profozich helped manufacturing companies from the Fortune 500 to the small, independents significantly improve their productivity and competitiveness.

